Apr 30, 2012
US hospital antiviral prescribing for flu dropped in year after pandemic
Antiviral use among hospitalized patients dropped significantly nationwide during the 2010-11 flu season compared with during the pandemic the year before, US researchers reported in Clinical Infectious Diseases. Using statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Influenza Surveillance Network, they noted that data on antiviral use was available for 99% of hospitalized patients with lab-confirmed flu in both seasons. During the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, 2,341 (77%) of 3,047 children and 4,754 (82%) of 5,819 adults hospitalized with flu received antiviral treatment. In 2010-11 those percentages dropped to 56% and 77%, respectively, with 763 of 1,365 children and 3,600 of 4,675 adults hospitalized with flu receiving antivirals. Both drops were statistically significant, they reported. The authors note that antiviral drugs are recommended for all hospitalized flu patients.
Apr 27 Clin
Infect Dis abstract
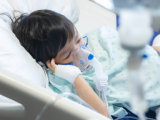
Study finds substantial cost burden of flu in young kids
Family out-of-pocket and indirect costs of lab-confirmed flu in young children is substantial and higher than previously thought, according to a study in Vaccine. The study involved data from the 2003-04 flu season at CDC New Vaccine Surveillance Network sites in Rochester, N.Y., Nashville, Tenn., and Cincinnati, Ohio. Researchers based their cost estimates on 2009 dollars. They explored expense data from parents of 67 hospitalized children under age 5, 121 kids who were treated for flu in the emergency department (ED), and 92 who received outpatient care. The burden was greatest in the hospitalized group. In that subset, caregivers missed about 73 work hours ($1,456). Parents of children treated in the ED and outpatient clinics missed 19 ($383) and 11 ($222) hours, respectively. Likewise, average out-of-pocket and indirect costs, ranging from $173 to $52, were highest for families of hospitalized patients and lowest for
those of kids treated at clinics. Those expenses were similar for patients with and without underlying medical conditions. Medical costs for caregivers of hospitalized kids was $3,990; for those treated in the ED, the cost was $730. The authors noted that their estimates were higher than in other reports.
Apr 27 Vaccine study
Workshop will address lessons of the H5N1 research controversy
A public workshop to be hosted by the National Academies tomorrow will address the implications of the controversy over two studies describing lab-modified H5N1 viruses with increased transmissibility. The workshop, called "Issues Raised, Lessons Learned, and Paths Forward for Dual-Use Research in the Life Sciences: The H5N1 Research Controversy," will be streamed over the Web. The event is designed to permit many stakeholders, including policymakers, biosecurity experts, nongovernmental organizations, international organizations, and the public, to air their concerns. Sessions will cover the revolution in the life sciences, two case studies involving dual-use research, a discussion on "the nature of the social contract," and a discussion on "governance, oversight, and the path forward."
National Academies information on the
event