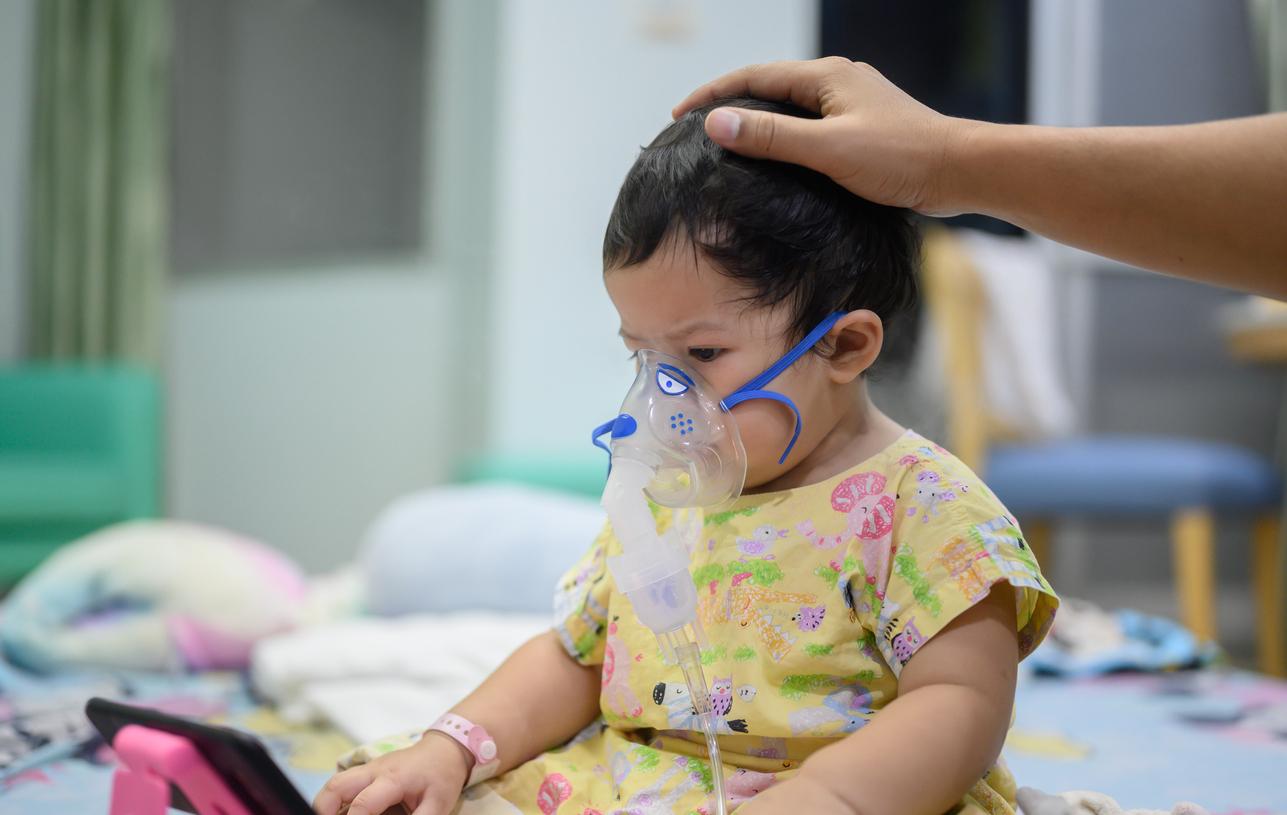
In its weekly flu season update today, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said though activity remains low nationally, there are slight increases in children, along with the first confirmed pediatric flu death of the 2024-25 season.
A few markers showed small increases last week, including percent positivity, which remains below the national baseline. Emergency department visits for flu increased a bit in pediatric age-groups.
Of two child flu deaths reported to the CDC this week, one was reported from February and was added to the previous season's pediatric deaths, which are now at 204. The other occurred in the middle of October and was related to an unsubtyped influenza A virus.
In updates on other respiratory viruses, today the CDC said COVID-19 activity is stable and declining in most areas. Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 levels remain low and are highest in the Midwest. Tracking by WastewaterSCAN, a national wastewater monitoring system based at Stanford University in partnership with Emory University, shows virus detections in the low category, with a downward trend over the past 3 weeks.
Shifting COVID variant proportions, rising RSV activity
In a SARS-COV-2 variant update today, the CDC reported the first decline in KP.3.1.1 proportions, which dropped from 57% to 52% over the past 2 weeks. Meanwhile, the proportion of XEC, a recombinant of two JN.1 viruses, continued a steady rise, up from 17% to 28% over the same period.
Another variant, called MC.1, also showed increasing proportions. In an update last week from the CDC's National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, the group said MC.1 is a descendant of KP.3.1.1 and that the updated vaccine is expected to work well against new variants that may become dominant, including XEC and MC.1.
Regarding respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), the CDC said it is seeing signs of rising activity in the southern, southeastern, and middle Atlantic regions, especially in young children.