Jun 17, 2010
As cases rise, Subway apologizes for Salmonella problems
Health officials in Illinois today said they have received 6 more reports of Salmonella serotype Hvittingfoss infections, raising the total to 86 cases so far. The number of affected counties remained at 26. Meanwhile, though the ongoing investigation has not found the outbreak strain in any Subway food products, the company yesterday issued an apology for the outbreak, the Associated Press (AP) reported. Corporate spokesman Kevin Kane added that all cases reported by the health department ate at the restaurants before Jun 3, and since then the stores have discarded and replaced lettuce, green peppers, red onion, and tomatoes.
Jul 17 Illinois Department of Public Health update
Jul 16 AP story
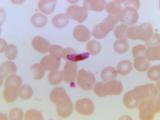
Malaria studies find new environmental and genetic clues
Clearing tropical forests in Brazil has boosted the incidence of malaria by almost 50%, researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison reported yesterday in Emerging Infectious Diseases (EID). Deforestation creates wide open spaces and partially sunlit pools of water that are an ideal habitat for the Anopheles darlingi mosquito that transmits the parasite in the regions of the Amazon, researchers reported. They also said A darlingi can displace other mosquitoes that prefer the forest and are less likely to spread malaria. The group compared high-resolution satellite data documenting changes in land cover with health data, correlating a 4% change in tree cover with a 48% increase in malaria incidence in 54 health districts. In other malaria research developments, an international team has identified a genetic risk factor for the development of cerebral malaria, a severe manifestation of the disease, in children from Angola. They reported their findings yesterday in Public Library of Science (PLoS) One. Experts have known that genetic factors can guide how individuals respond to malaria infections, but little is known about susceptibility to certain complications. Investigators compared a series of genetic variations between malaria patients who did and didn't develop the cerebral complication. They found that variants in two genes, TGFB2 and HMOX, were linked to greater risk of developing cerebral malaria.
Jun 16 EID study
Jun 16 PLoS One study
Groups to launch new polio strategy
The World Health Organization (WHO) is hosting a meeting in Geneva tomorrow to unveil a new 2-year polio eradication strategy and to discuss how to address a funding shortfall of $1.3 billion over the next 3 years, nearly half of its budget. In a press release, the WHO said the polio eradication efforts are at a critical juncture. It said 10 of 15 previously polio-free African countries that were reinfected in 2009 have stopped the outbreaks, but said a recent outbreak in Tajikistan highlights the importance of keeping eradiction momentum going. Tomorrow's meeting will be attended by a range of stakeholders, including country health ministers, current and potential funding groups, vaccine manufacturers, and key partners such as Rotary International and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Jun 17 WHO press release