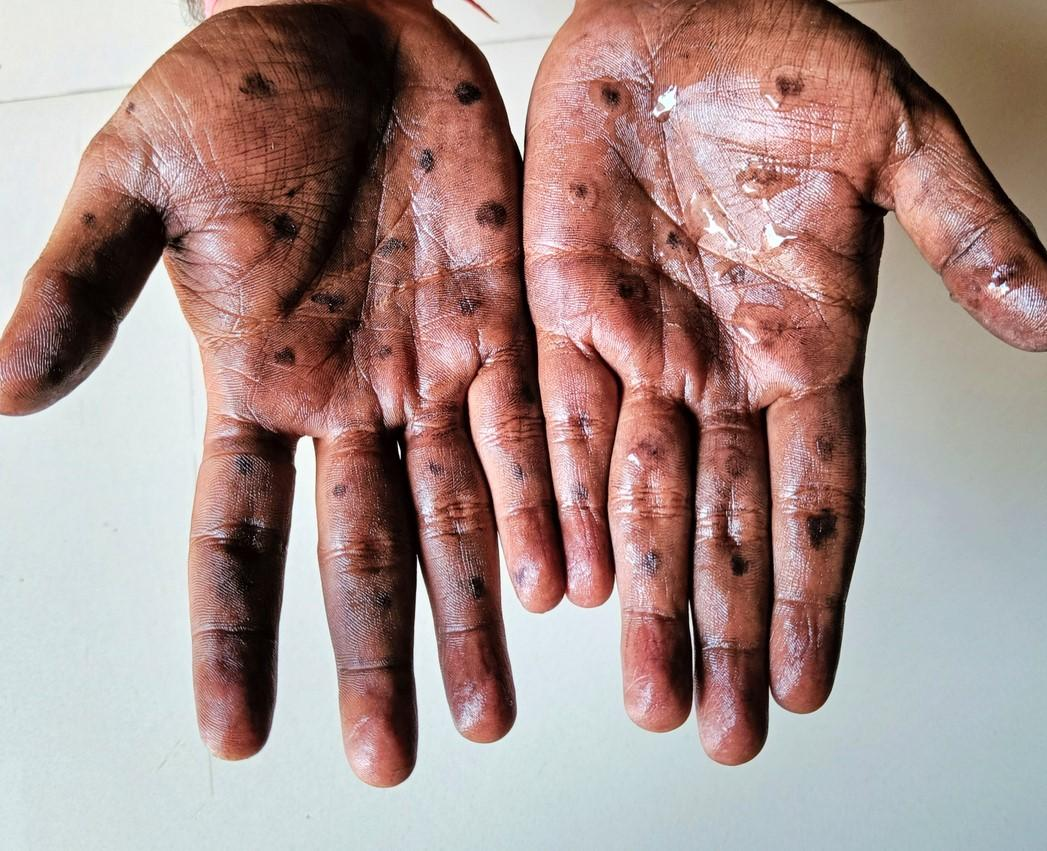
A meta-analysis of papers published during mpox epidemics from 1970 to 2023 suggests that symptoms in affected patients have become more diverse, with a decrease in symptoms other than rash.
Researchers from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University in China searched three databases for English-language, peer-reviewed studies on mpox symptoms published from January 1970 to April 2023. The periods covered included 1970 to 2022 (period 1, within Africa), 2003 to 2021 (period 2, mostly within Africa, but clusters elsewhere), and 2022 to 2023 (period 3, worldwide).
The 61 included studies reported on 21 symptoms in 720 mpox patients from period 1, 39 symptoms from 1,756 patients from period 2, and 37 symptoms from 12,277 patients from period 3.
The findings were published late last week in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.
Rash common to all 3 periods
The most common symptom in all three periods was rash (period 1, 92.6%; period 2, 100%; and period 3, 94.8%), followed by enlarged lymph nodes (period 1, 59.8%; period 2, 74.1%; and period 3, 61.1%). In period 1, the primary symptoms were fever (99%), enlarged lymph nodes (80.5%), and headache (69.1%), with a significant decline in these symptoms in period 3 (37.9%, 31.2%, and 28.7%, respectively).
Epidemic countries may shift their focus on the potential association among symptoms and the high synergy risk.
In period 2, chills/shivering (73.3%), fatigue (68.2%), and difficulty swallowing (61.2%) emerged as the main symptoms but fell off significantly in period 3. In period 3, most other symptoms were similarly prevalent or declined relative to periods 1 and 2.
Nausea/vomiting correlated most closely with 13 symptoms and was highly positively correlated with enlarged lymph nodes and conjunctivitis ("pink eye") in period 2. During period 3, rash and headache were both most closely correlated with 21 symptoms and were highly positively correlated with fever.
"It is necessary to surveil the evolving nature of mpox and the consequential changes in clinical characteristics," the study authors wrote. "Epidemic countries may shift their focus on the potential association among symptoms and the high synergy risk."